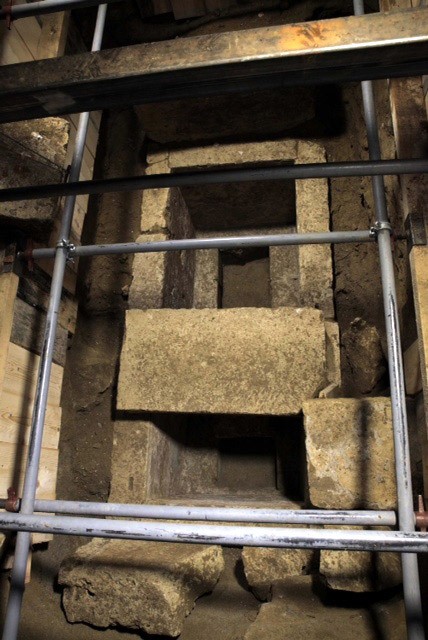
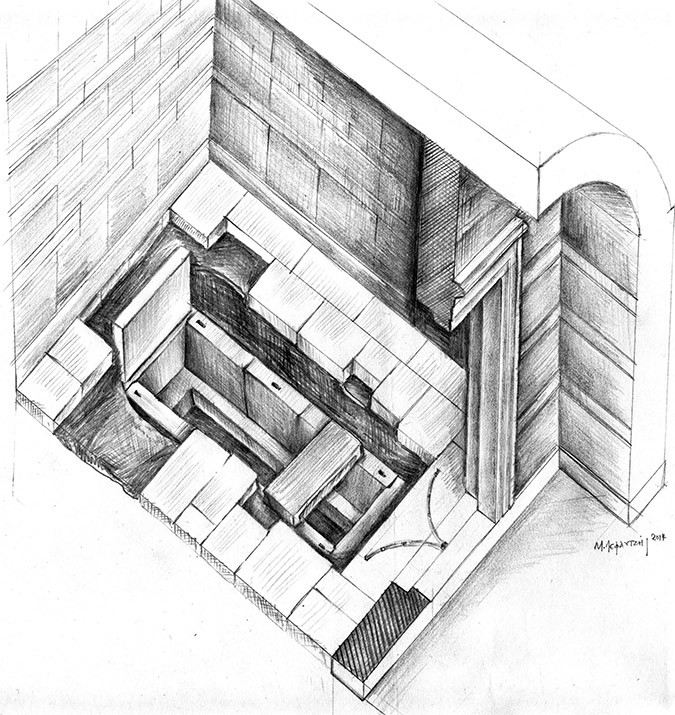
Archaeologists in northern Greece announced on Wednesday that they found a skeleton belonging to a distinguished ancient celebrity from the time of Alexander the Great in the ancient tomb at Amphipolis. Chief archaeologist Katerina Peristeri speculated that “the tomb in all probability belongs to a male and a general.”
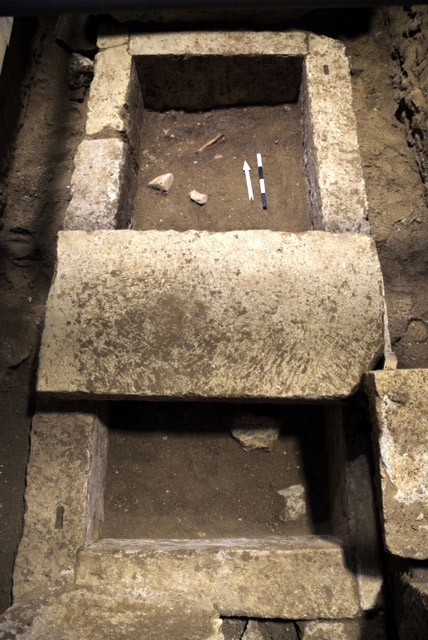
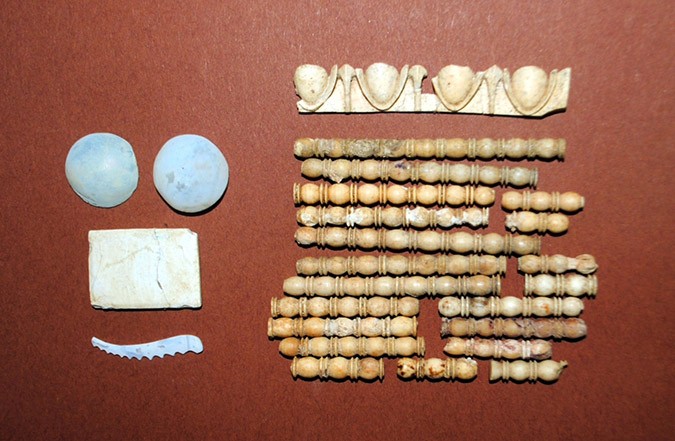
The skeleton found is housed in a wooden coffin once held together by iron and bronze nails and studded with bone and glass decorations. Though the coffin has disintegrated over time, the skeletal remains are intact and were found both inside and outside the floor of the tomb, possibly as a result of the looting during ancient times.
Archaeologists estimate that the person whose remains were found was 1.8 meters tall, however there will need to be complex lab work and an analysis of organic residue that could take months to complete before having a clearer picture of the occupant of the tomb. The analysis will allow archaeologists to restrict the number of potential candidates that the tomb belongs to rather than point to a single person with certainty, possibly Nearchos or Hephaistion, or even Alexander the Great, event though finding the latter is unlikely if historical sources are taken into account.
An analysis of the bone structure will give a clearer idea of the occupant’s build, health and injuries they may have had during their lives that could give scientists more clues when pinpointing the identity of the occupant of the tomb.
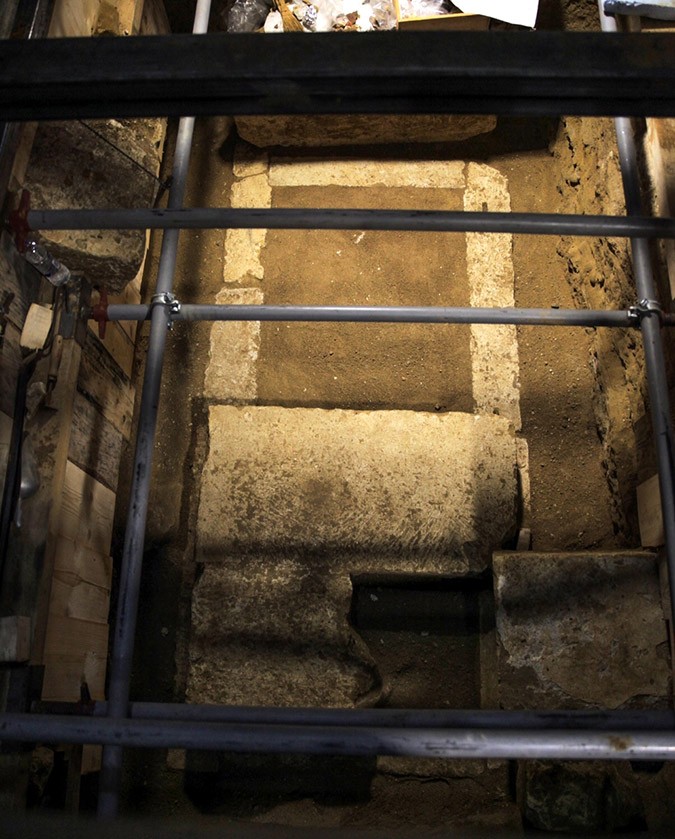
The announcement of the discovery of the skeleton overshadowed any other discussion on the monument and a number of serious questions remain unanswered. For instance, the question as to why the monument was sealed even though it had been looted. Furthermore, there is a strong contrast between the pre-chambers and size of the monument compared to the no-frills decor in the main burial chamber and the frugal space in the underground cist grave where the skeleton was found.
Take the tour –
Amphipolis Tomb by Greektoys.org (new update #3)
by Greektoys.org
on Sketchfab
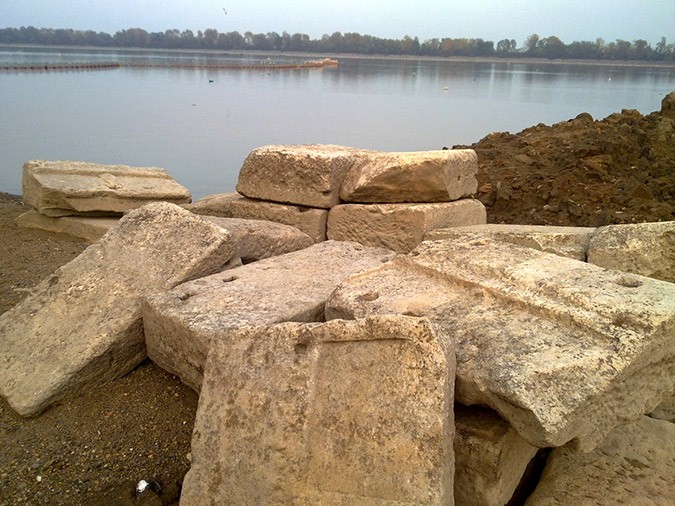
The excitement of finding the skeleton dominated the discussion, however noteworth is the fact that over 500 pieces of the surrounding wall were found near the place where the Lion of Amphipolis sits. More than 100 stones were discovered just a couple of days ago in Lake Kerkini where the pieces were transferred in 1936 by the company Ulen who were responsible for the construction of the Dam at Kerkini.
Ask me anything
Explore related questions