The United Nations has released a new report focusing on water, sanitation, and hygiene around the world. It has found that approximately 2.2 billion people worldwide lack access to safe drinking water, 4.2 billion have to go without safe sanitation services and three billion lack basic handwashing facilities. The report also examined the state of open defecation and progress in eliminating it. As recently as 2015, close to a billion people were still defecating outdoors, resulting in widespread disease and millions of deaths. That drove the UN to call for an end to the practice and some parts of the world have proven hugely successful in eradicating it.
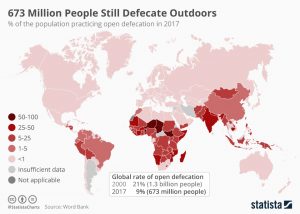
In 2000 for example, the rate of open defecation was even worse with 21 percent of the global population – 1.3 billion people – practicing it. The impact of the UN’s call to action has been telling and by 2017, the global share of people practicing open defecation had fallen to just 9 percent – 673 million people. Ethiopia saw the largest fall during that period, -57 percent. Cambodia and India also experienced declines of -53 and -47 percent respectively. The latter has been particularly ambitious in installing proper toilets. Before Prime Minister Narendra Modi came to power, just under 40 percent of India’s population had access to a household toilet. He promised to change that and billions of dollars were invested under the Swachh Bharat Abhiyan (“Clean India”) campaign which kicked off in October 2014. India’s Ministry of Drinking Water and Sanitation states that toilet coverage today stands at an impressive 99.22 percent.
Altogether, 91 countries reduced open defecation by a combined total of 696 million people between 2000 and 2017 with Central and Southern Asia accounting for three-quarters of that figure. The news isn’t positive everywhere though and 39 countries experienced increases during the same period, totaling 49 million people. The majority of that increase occurred in Sub-Sahara Africa which has experienced steady population growth since 2000. That, of course, means that there’s still a lot of work to do but as India has shown with its toilet building marathon, progress can be rapid.
source: statista
Ask me anything
Explore related questions





