Egyptian billionaire Naguib Sawiris recently announced plans to buy a Greek island to give refugees from the Middle East and Africa a country of their own. Though Sawiris referred to his proposal as a “crazy idea” on Twitter, it pales in comparison to an earlier scheme for the Mediterranean from the first half of the 20th century, which was seriously considered by heads of state and, at one point, even the United Nations. It was called Atlantropa, and would have involved the partial draining of the Mediterranean Sea and the creation of a Eurafrican supercontinent.
Atlantropa was the brainchild of the German architect Herman Sörgel, who tirelessly promoted his project from 1928 until his death in 1952. His experience of World War I, the economic and political turmoil of the 1920s and the rise of Nazism in Germany convinced Sörgel that a new world war could only be avoided if a radical solution was found to European problems of unemployment, overpopulation and, with Saudi oil still a decade away, an impending energy crisis. With little faith in politics, Sörgel turned to technology.
Americans searching “Greece” more than any European destination
Twitter advocates freedom of internet and expression for Ugandan elections…
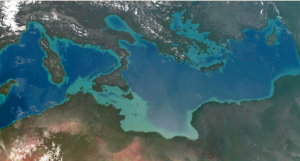
Dams across the Strait of Gibraltar, the Dardanelles, and eventually between Sicily and Tunisia, each containing gigantic hydroelectric power plants, would form the basis for the new supercontinent. In its final state the Mediterranean would be converted into two basins, with the western part lowered by 100 meters and the eastern part by 200 meters and a total of 660,200 km2 of new land reclaimed from the sea – an area larger than France.
Read more: the conversation
Ask me anything
Explore related questions