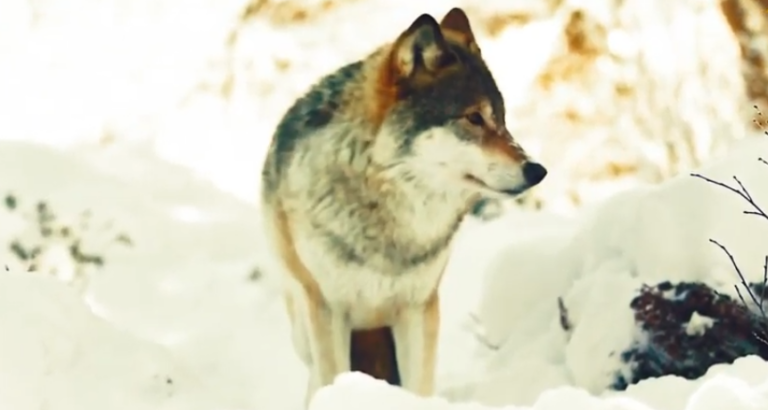
The domestication of dogs is a fascinating topic that has puzzled scientists for decades. The evolution of wolves into our beloved pets is a remarkable feat, and understanding how this process took place can provide insight into the history of our relationship with animals. From guard dogs to hunting partners, domestic dogs have played various roles throughout human history, and in this article, we’ll explore five intriguing facts about how wolves were turned into ancient pets.
The domestication of dogs occurred over 15,000 years ago, during the Paleolithic era. During this time, wolves began to scavenge near human settlements, drawn by the availability of food. Over time, the wolves became more comfortable around humans, and it’s thought that humans began to tame and breed them for certain desirable traits. This led to the development of different dog breeds each with their unique set of skills and characteristics.
Stunning Roman villas unearthed in underwater ruins of ancient Baiae
Source: Ancient Origins
Ask me anything
Explore related questions