A scientific team in the Netherlands was studying prostate cancer when they stumbled upon something exciting at the other end of the body.
Specifically, the researchers were working at the Dutch Cancer Institute and conducting a series of CT scans and PET scans on patients who had been administered radioactive glucose.
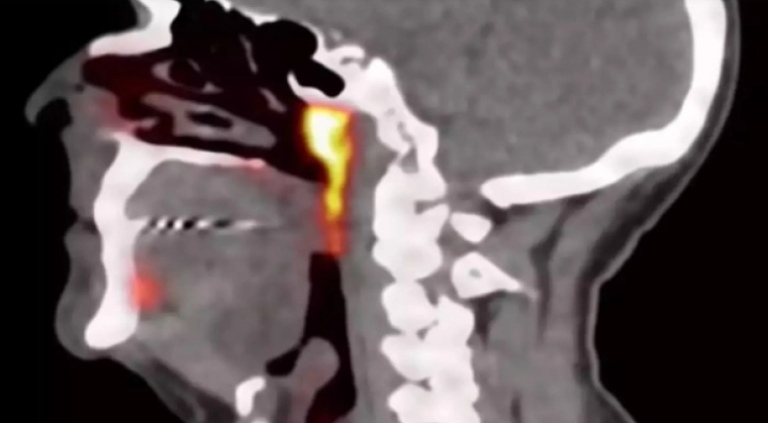
They didn’t do this randomly. They knew very well that glucose would make tumors “light up” on the scans and be more easily detectable.
This particular substance is also very good for detecting salivary glands. So, when they examined the results, specialists noticed that some areas inside the human head were also lighting up, which intrigued them. Carefully examining the research results, they found that there are some salivary glands behind the nose and near the point where the nasal cavity meets the throat. Specialists believe that these particular glands lubricate your throat behind your nose and mouth. The Dutch team named it the “tubarial salivary gland”.
Then, to confirm, they examined 100 patients and verified that all of them have one such gland behind their nose.
The human body has three other important salivary glands, all located in the head, except for one where the tubarial glands are.
The parotid glands are the largest and provide the saliva that helps you chew and swallow your food.
Underneath the lower jaw are the submandibular glands, which are responsible for producing most of the saliva in your mouth.
Lastly, and possibly less significant, are the sublingual glands located beneath the tongue.
Ask me anything
Explore related questions