Since the Luna 3 spacecraft first photographed the Moon’s far side in 1959, scientists have wondered why its two hemispheres differ dramatically. The near side is covered with large lava plains, while the far side is dominated by craters and rough terrain.
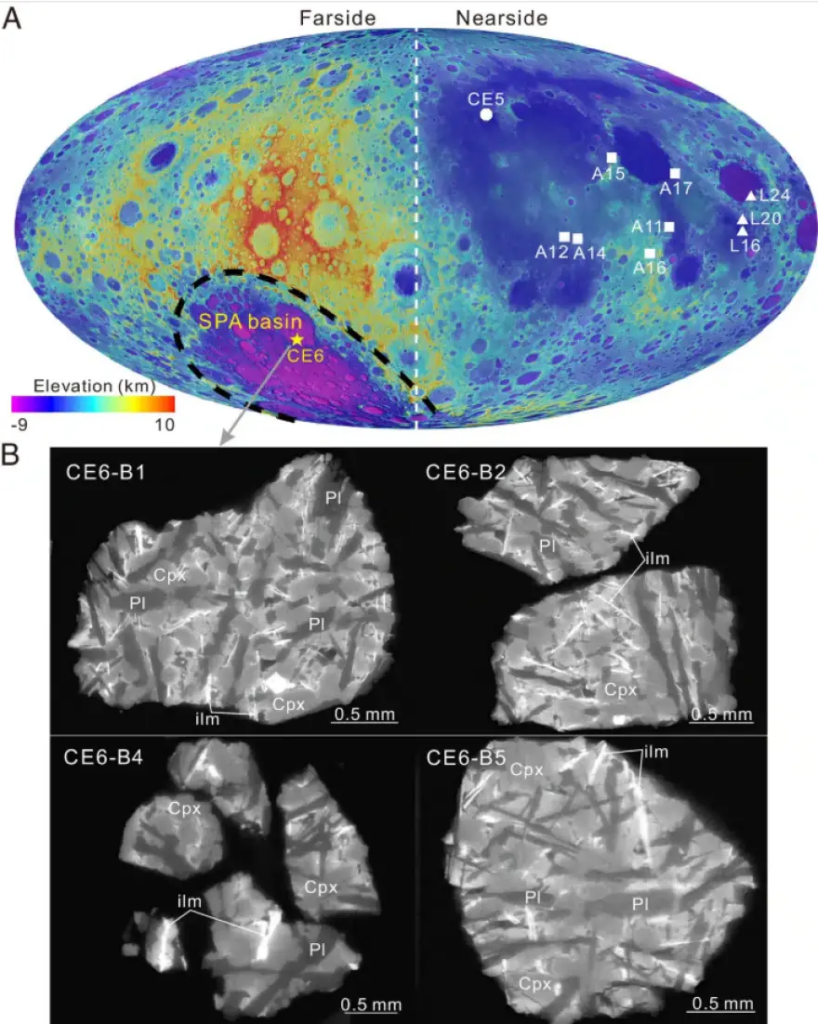
Until recently, no physical samples had been collected from the far side to study its composition directly. This changed with China’s Chang’e-6 mission, which returned dust samples from the South Pole–Aitken basin—a massive crater formed by one of the largest impacts in the Solar System.

Scientists analyzed isotopes of potassium and iron in these samples and found a clear excess of heavier isotopes on the far side compared to the near side. This difference cannot be explained by volcanic activity alone.
The findings suggest that the colossal impact that formed the South Pole–Aitken basin generated extreme heat, causing lighter isotopes to evaporate and leaving behind a “heavier” chemical signature. Moreover, the impact likely penetrated deep into the Moon’s mantle, reshaping its internal structure.
These results offer a key to understanding how ancient cosmic collisions influenced not only the Moon’s surface but also its interior. Such events may have permanently altered the Moon’s mantle circulation and composition.
This discovery marks a significant step in unraveling a decades-old mystery and enriches our understanding of how planetary bodies evolve after massive impacts.
Ask me anything
Explore related questions





