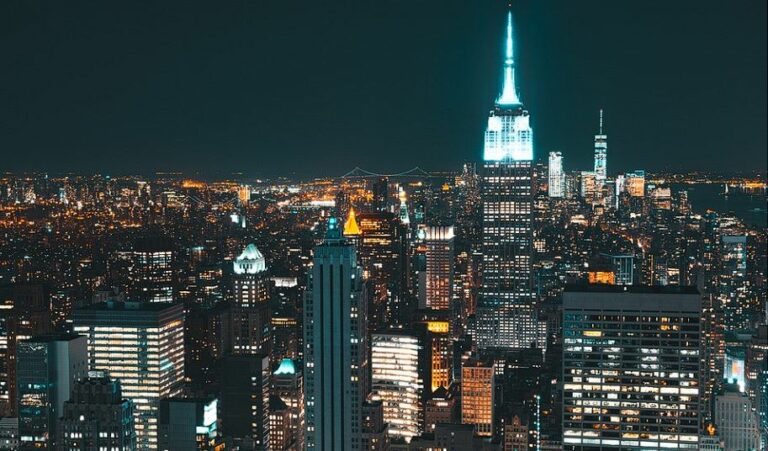
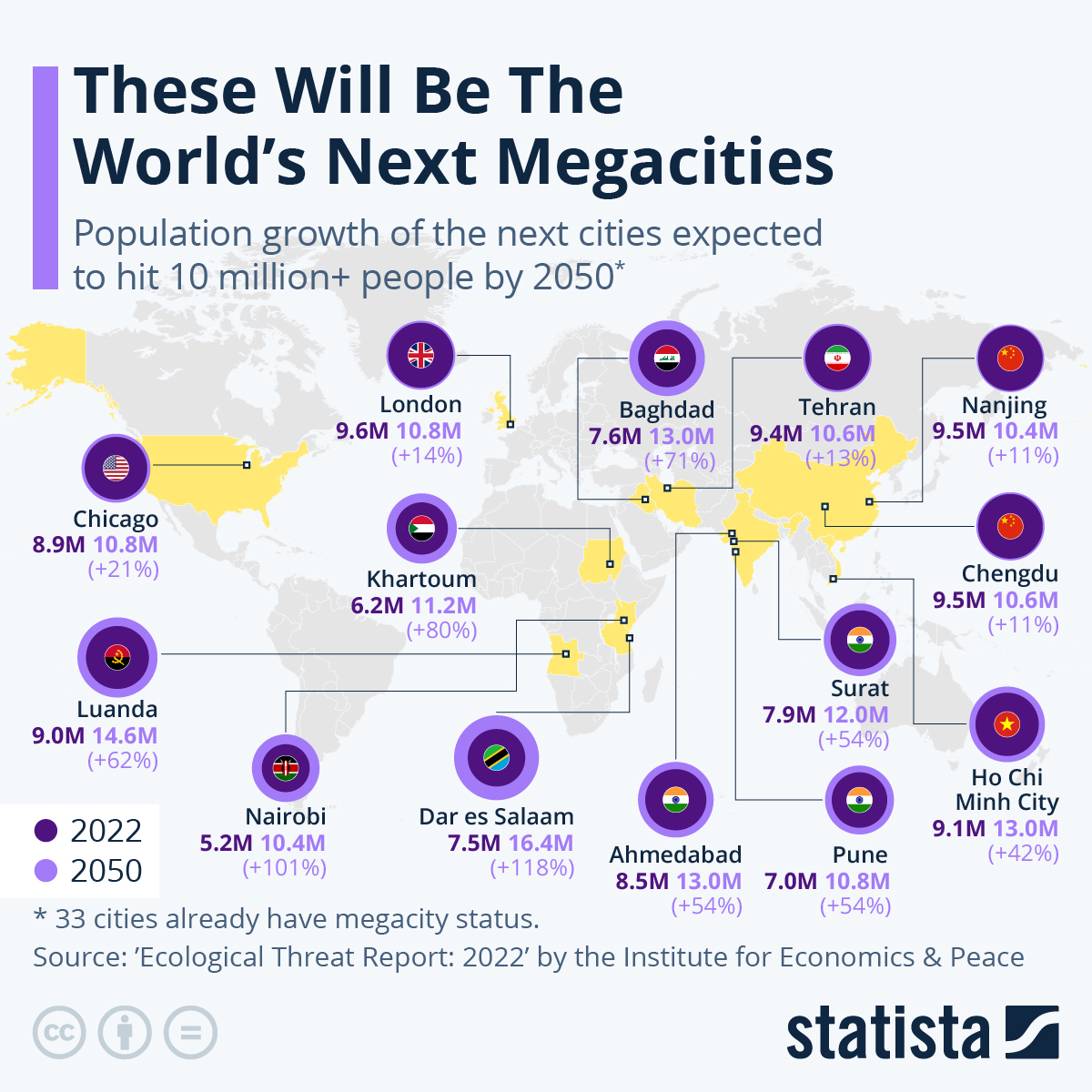
By 2050, 70 percent of the world’s population will live in cities, up from 54 percent in 2020, according to a new report by the Institute for Economics & Peace. This increase is being driven by both population growth and a continued shift towards urbanization, particularly to so called ‘megacities’ – metropolises that have a population of 10 million or more.
Urbanization takes place because of both push and pull factors. The IEA describes how in the Democratic Republic of Congo’s capital of Kinshasa, factors pushing people away from rural areas include issues of violence and a general lack of security, the presence of criminal groups, lack of policing, ecological degradation, and the fact there are too many people for the available agricultural land. Meanwhile, a pull factor could be the attraction of an increase in the standard of living.
There are currently 33 megacities worldwide. Tokyo (37.3 million), Delhi (32.3 million), Shanghai (28.7 million), Dhaka (22.6 million), São Paulo (22.5 million) and Mexico City (22.1 million) take the lead as the most populous of these. By 2050, 14 more cities are set to join their ranks, with a total increased population of some 213 million people. The new order will then become Delhi (49.6 million), Dhaka (34.6 million), Tokyo (32.6 million), Cairo (32.6 million) and Mumbai (32.4 million).
In addition to a rise in the number of people living in these cities, the countries themselves will also likely see economic growth. According to AXA, Manila in the Philippines and Bangalore in India are expected to see close to 150 percent GDP growth by the end of the decade.
Africa is the only world region expected to still see strong population growth by the end of the century, according to the Pew Research Center, while all other regions’ growth rates will start to tail off. This is reflected in our chart, as it’s notably the African megacities that will see the biggest population rate increases. Meanwhile, only three megacities will see decreases in their population size: the Russian capital of Moscow (-3 percent), and Japan’s Osaka (-12 percent) and Tokyo (-12 percent). Despite Tokyo’s shrinkage, brought on by an aging population and declining birth rate, the capital will still rank as the world’s fourth most populated megacity in 2050.
The 33 cities that have already hit megacity status are the following: Delhi, Dhaka, Cairo, Tokyo, Mumbai, Shanghai, Kinshasa, Lagos, Karachi, Mexico City, São Paulo, Beijing, Kolkata, New York City, Manila, Lahore, Bangalore, Chongqing, Buenos Aires, Osaka, Hyderabad, Tianjin, Guangzhou, Los Angeles, Rio de Janeiro, Bangkok, Jakarta, Shenzhen, Lima, Paris and Moscow.
It’s important to note here that different sources cite different statistics, and that especially with forecasts, situations can change. For instance, where the United Nations initially predicted that India would overtake China as the biggest country in 2027, it is now expected to take place in April of this year. In terms of megacity status, according to UN data from 2018, several additional cities, including Kuala Lumpur in Malaysia and Wuhan in China, will make the roundup even by 2035. Read more on the nature of conflicting reports here.
You will find more infographics at Statista
Ask me anything
Explore related questions