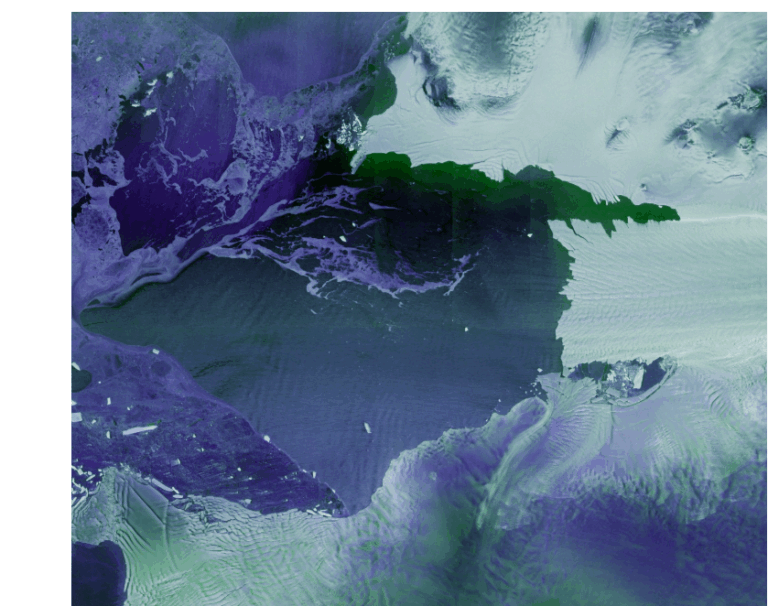
Glaciers in Antarctica and Tierra del Fuego at the southern tip of South America are included in the first high-resolution images captured by the Copernicus Sentinel-1D satellite. These images were presented for the first time at the Council of Ministers meeting of the European Space Agency (ESA) held yesterday in Bremen, Germany.

Once in orbit, the satellite and its instruments, including a 12-meter synthetic aperture radar (SAR), were activated to capture images as it passed over Antarctica and South America two days after launch. On the night of November 6th, the first images captured the Thwaites Glacier in Antarctica and Tierra del Fuego. The data were then transmitted from the satellite to the ground station in Matera, Italy, part of the Copernicus ground segment. All of this was accomplished within approximately 50 hours from launch—a timeframe that ESA’s press release suggests is likely a new record for radar Earth observation satellites from launch to data delivery.
The radar instruments onboard can image the Earth’s surface regardless of weather conditions or daylight, making them ideal for monitoring polar regions. Sentinel-1C and 1D also carry an Automatic Identification System (AIS) that enhances the mission’s ability to detect ships and marine pollution.
A photo of the Thwaites Glacier and neighboring Pine Island Glacier, located west of the Antarctic Peninsula, shows sea ice in shades of purple and glaciers in white. The detailed images from Sentinel-1D highlight the fragility of glaciers in the face of climate change. The year 2025 has been declared the International Year of Glacier Protection by the United Nations.
Nuno Miranda, director of ESA’s Sentinel-1 mission, emphasizes the unprecedented quality of data in this initial capture, adding:
“These images were transmitted and processed in an extraordinarily short period. When Sentinel-1B was launched, it delivered the first radar images within two hours of activation. Sentinel-1D accomplished this even faster, setting what we believe to be a new record for spaceborne radar.”
This breakthrough in satellite imaging represents a crucial tool for monitoring vulnerable glacial environments and underscores the urgent need for global climate action to protect these essential natural resources.
Ask me anything
Explore related questions