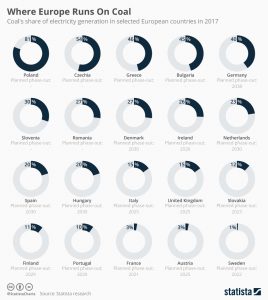
Greece is generating nearly 50% of its electricity from coal. The end of the age of fossil fuels is not yet in sight in Europe. As this infographic shows, there are still a number of countries that generate a very large proportion of their electricity from coal. At the same time, not all countries have announced a date for phasing out its use. This applies in particular to those countries that have a high proportion of coal-fired electricity. Despite recent efforts to transition to renewable energy, Germany still lies in the upper quarter of the country comparison, behind countries such as Poland, Czechia, and Bulgaria. The government is aiming to phase out coal by 2038.
Scientists are demanding a move away from electricity generation from coal. The prevention of climate change can only be achieved by a complete abandonment of fossil fuels. In addition, electricity from renewable energies can be produced more cheaply than electricity from fossil fuels – taking into account the resulting costs of health and climate damage. In Poland, for example, many people suffer health problems from the consequences of high levels of air pollution. Nevertheless, there is no prospect of a swift turn away from coal. One reason for this is that jobs in the five-digit region depend on coal production.
Global coal production has risen again recently, with around 8 billion tonnes of coal mined in 2018. Countries such as China, Russia and the USA contributed to the increase.
source statista
Ask me anything
Explore related questions





