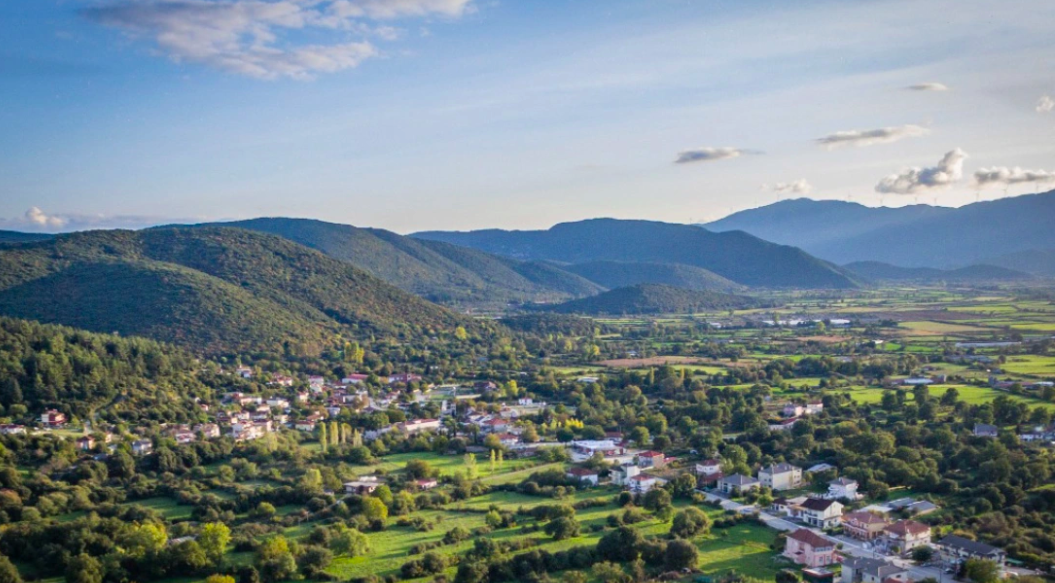
Researchers at Democritus University of Thrace have launched a groundbreaking program, EpiSafeNet, aimed at flood risk assessment and management in the Epirus region. This initiative focuses on rivers such as Arachthos, Aoos, and Louros, which are prone to frequent and destructive flooding. The team, led by Professor Dimitris Emmanouloudis, has utilized advanced technology, including AI, machine learning, and multi-criteria analysis, to predict flood behavior with remarkable precision.
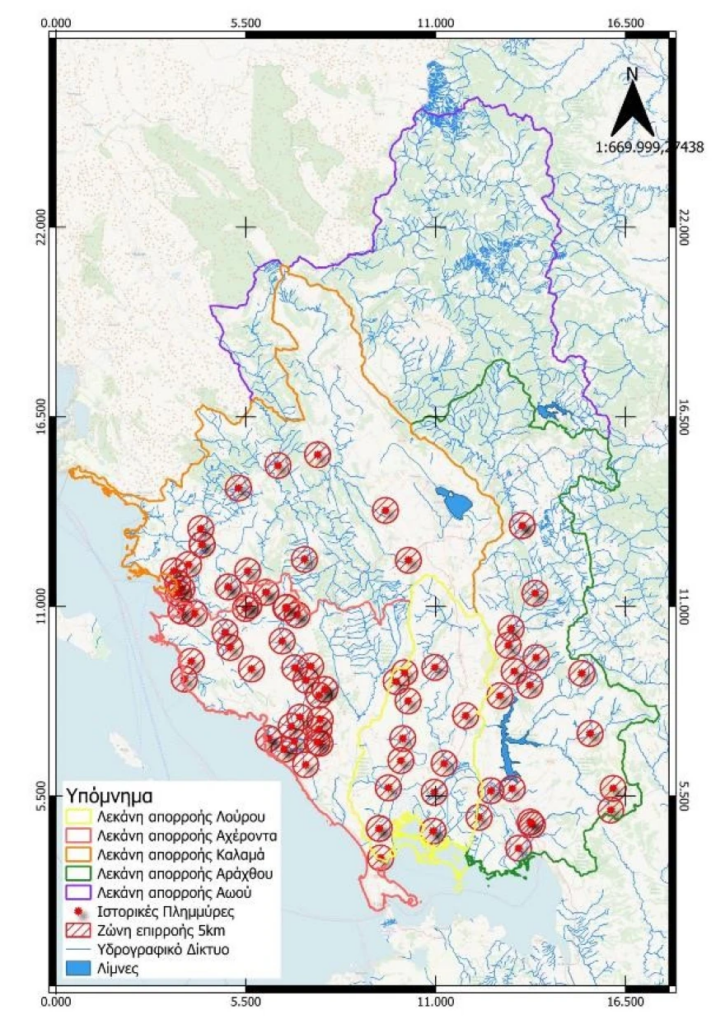
The program employs a combination of forecasting, hydrological, and hydraulic simulations to map flood risks. It helps authorities better understand rainfall patterns, water movement, and flood-prone zones. By using 3D river visualizations, the team trains machine learning models to predict how water behaves in different flood scenarios and informs strategic decisions for protective infrastructure.
Key focus areas like Parga and Sivota—where both residential development and tourist activity are concentrated—have been closely monitored. This predictive tool also creates flood risk maps, indicating where evacuations should occur. These insights will help with the effective placement of flood prevention infrastructure and facilitate timely evacuation planning.
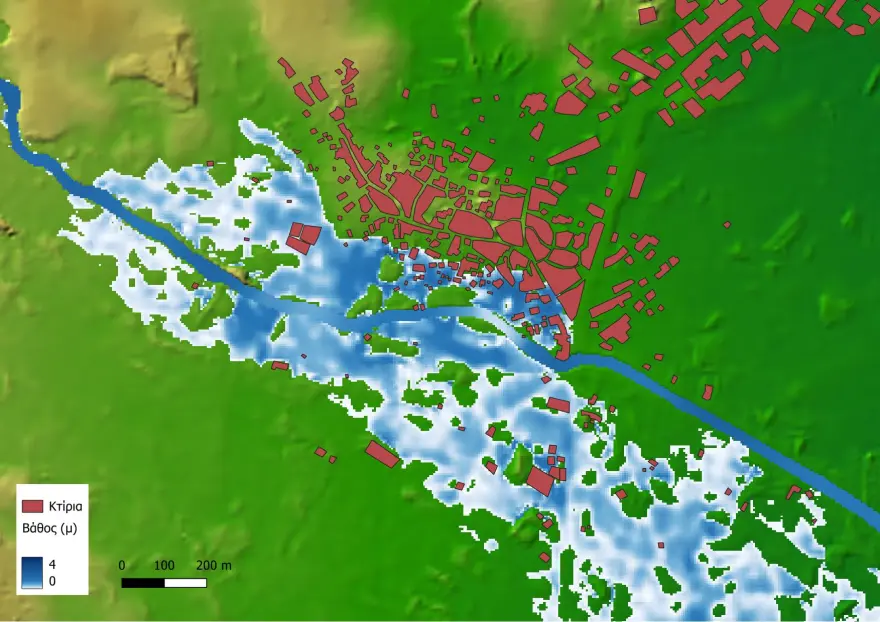
While this research is vital for managing flood risks in Epirus, its application has great potential for similar flood-prone regions, including Attica. The EpiSafeNet project serves as a model for how advanced technologies can inform and improve flood preparedness and disaster management strategies across Greece.
Ask me anything
Explore related questions





