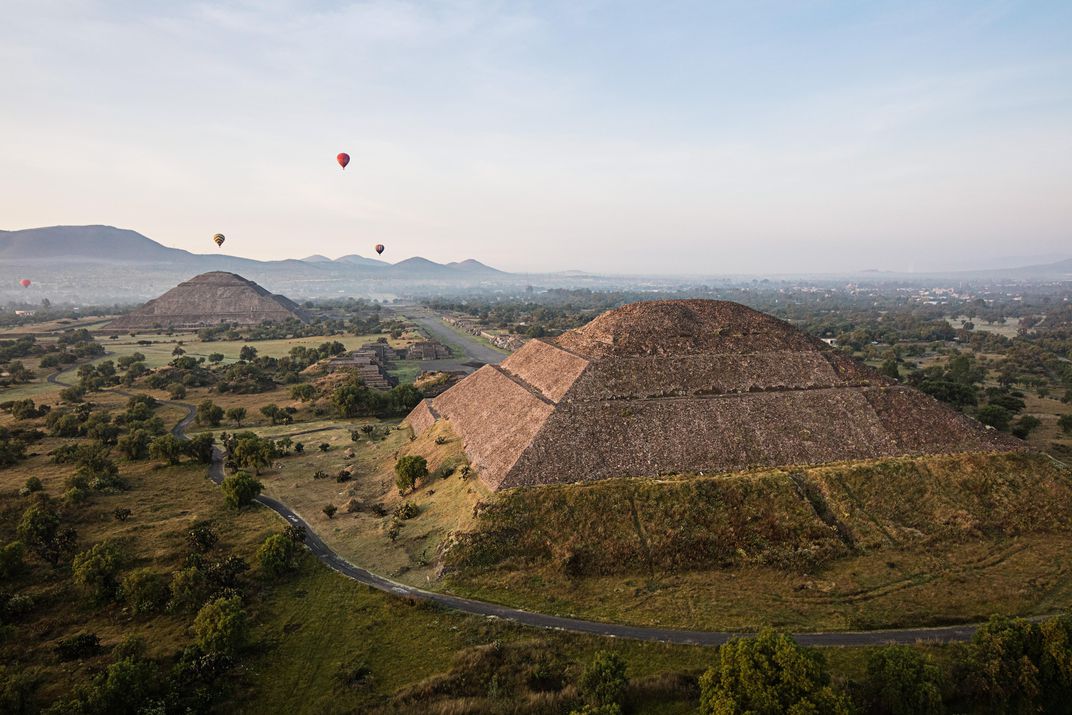
In the fall of 2003, a heavy rainstorm swept through the ruins of Teotihuacán, the pyramid-studded, pre-Aztec metropolis 30 miles northeast of present-day Mexico City. Dig sites sloshed over with water; a torrent of mud and debris coursed past rows of souvenir stands at the main entrance. The grounds of the city’s central courtyard buckled and broke. One morning, Sergio Gómez, an archaeologist with Mexico’s National Institute of Anthropology and History, arrived at work to find a nearly three-foot-wide sinkhole had opened at the foot of a large pyramid known as the Temple of the Plumed Serpent, in Teotihuacán’s southeast quadrant.
“My first thought was, ‘What exactly am I looking at?’” Gómez told me recently. “The second was, ‘How exactly are we going to fix this?’”

Gómez is wiry and small, with pronounced cheekbones, nicotine-stained fingers and a helmet of dense black hair that adds a couple of inches to his height. He has spent the past three decades—almost all of his professional career—working in and around Teotihuacán, which once, long ago, served as a cosmopolitan center of the Mesoamerican world. He is fond of saying that there are few living humans who know the place as intimately as he does.
Read Also:
President Sakellaropoulou: “In order for national effort to succeed, ‘we’ must come before ‘I’”
EU summit to ratify start of accession talks for Albania & North Macedonia
Coronavirus: Scientists photographed Covid-19 & these are the first microscope images (photos)
And as far as he was concerned, there wasn’t anything beneath the Temple of the Plumed Serpent beyond dirt, fossils and rock. Gómez fetched a flashlight from his truck and aimed it into the sinkhole. Nothing: only darkness. So he tied a line of heavy rope around his waist and, with several colleagues holding onto the other end, he descended into the murk.
Read more: smithsonian
Ask me anything
Explore related questions