Toxic waste produced by one of the world’s worst nuclear disasters will be dumped into the sea, according to the head of the Japanese company tasked with cleaning up the radioactive mess, despite protests from local fishermen.
Takashi Kawamura, chairman of Tokyo Electric Power Company (TEPCO), told foreign media that nearly 777,000 tons of water tainted with tritium, a byproduct of the nuclear process that is notoriously difficult to filter out of water, will be dumped into the Pacific Ocean as part of a multibillion-dollar recovery effort following the Fukushima nuclear disaster in 2011. That year, an earthquake and tsunami struck Japan, killing over 15,000 people and leading to a series of meltdowns at the TEPCO-owned Fukushima No. 1, or Daiichi, nuclear power plant, causing it to spew radiation that has plagued the region ever since. While much progress has been made to clean the area, the company has only just resolved the debate over what to do with the water that was used to cool the plant’s damaged reactors, causing it to become tainted with tritium.
“The decision has already been made,” Kawamura said, according to The Japan Times.
“We could have decided much earlier, and that is TEPCO’s responsibility,” he added, according to Reuters.
Tritium is relatively harmless to humans in small doses, and Japanese Nuclear Regulatory Agency Chairman Shunichi Tanaka told The Guardian last year that the tritium in Fukushima’s tanks was “so weak in its radioactivity it won’t penetrate plastic wrapping.” Dumping tritium-contaminated water into the sea is not at all an uncommon practice at nuclear power plants, but it’s been met with opposition by local fishermen, who say their industry has suffered enough in the aftermath of the environmental crisis.
While TEPCO and Tokyo say that the low concentration of tritium would do little damage to the ecosystem and could prevent a more serious accident from occurring at the site, where around 580 tanks are stored, fishermen argue that the negative publicity would be devastating to their livelihoods. Dozens of countries and the European Union now ban certain fish imports from Japan following the disaster, and up to 33 continue to do so as of March. TEPCO’s decision also has been met with outrage by anti-nuclear activists such as Aileen Mioko-Smith of Kyoto-based Green Action Japan, a group created in 1991 that is “working to create a nuclear-power-free Japan,” according to its official website.
“This accident happened more than six years ago, and the authorities should have been able to devise a way to remove the tritium instead of simply announcing that they are going to dump it into the ocean,” Mioko-Smith told the Telegraph.
“They say that it will be safe because the ocean is large so it will be diluted, but that sets a precedent that can be copied, essentially permitting anyone to dump nuclear waste into our seas,” she continued.
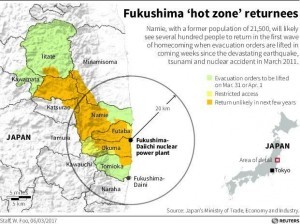
A map showing the status of restricted areas affected by radiation from the Fukushima No.1 nuclear plant as of March 6, 2017. The nuclear disaster displaced up to 150,000 people, and many are reluctant to return to the region, despite pressure from the Japanese government. Japan’s Ministry of Trade, Economy and Industry
TEPCO’s over-budget, oft-delayed effort to recover its former plant has been the subject of controversy for a number of reasons. Due to residual nuclear fuel, parts of the plant are so radioactive that they have even destroyed the robots specifically designed to survive in the deadly environment. Last month, Japanese company Toshiba announced it would send a new robot dubbed “little sunfish” to surveil the flooded area of the plant from which no device has returned, BBC News reported. A number of TEPCO officials have also stood trial for negligence over the nuclear disaster.
As for the rest of the Fukushima prefecture, life has started to resume, albeit slowly. Of the estimated 150,000 who fled, only around 13 percent have come back. The Japanese government has increasingly pressured the rest to return by pledging greater investment in Fukushima’s infrastructure and by withdrawing subsidies provided to the refugees and their families.
Ask me anything
Explore related questions