It’s been a while but eurozone finance ministers are grappling with another big fat Greek deadline.
The EU’s largest ever debtor nation is preparing to exit its bailout programme after eight years of cash drip feeds, unprecedented economic tutelage, and an economy that has suffered the worst depression of any nation in modern times. The momentous day of departure is August 20.
The Brussels Briefing has written before about the risks for eurozone governments of letting Greece go. With the bailout expiry imminent, it’s a quandary that will be front and centre of finance ministers’ minds as they gather in Sofia for the eurogroup on Friday.
The dilemma is thus: having kept Athens on a tight leash since 2010, how can eurozone capitals ensure the Greeks — who owe them over €200bn in taxpayer money — will keep paying them back over the next six decades?
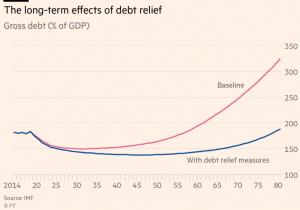
For the International Monetary Fund, the answer is a generous dose of debt relief to help Greece stay on a sound financial footing and ensure creditors aren’t stiffed when the next crisis comes. Eurozone governments — led by Germany — are reluctant. More debt relief means less money back for their taxpayers.
A new fight is brewing about how creditors should keep the strings attached once the bailout is over. The battleground is a “dynamic” debt relief mechanism designed to link repayments to economic performance. In bad times the bill is reduced; in boom times, the Greeks pay more.
Berlin and its northern allies — still scarred by the Syriza scare of 2015 — want the tool to come with strict conditions. Germany’s new finance minister Olaf Scholz is insisting the Bundestag sign-off on a debt relief decision every year. The hawks also want an effective break clause that would suspend the relief if Athens slips in meeting its post-programme conditions and budget targets.
Pushing back are France and the IMF who want an automatic system that gives no room for political discretion in Berlin. That’s the best way to assure investors the EU is serious about helping out Greece, they say.
No concrete decisions are due from finance ministers in Sofia on Friday but the two camps will need to thrash out a compromise soon. June is the deadline to finalise the terms of the bailout exit. The IMF needs the Europeans to move by May if it is to formally join the Greek programme.
At stake is the question of how to bind future governments for generations to come to the promises of the current regime. Brexit, anyone?
Source: FT
Ask me anything
Explore related questions