More than one in three Greeks, compared to an average of one in five in the EU, live in poverty or social exclusion, according to Eurostat data published in 2017.
In Greece, 34.8% of the population was in 2017 on the brink of poverty or social exclusion, 3.7 million people, compared to 28.1% in 2008. At the same time, in the EU in 2017, this figure dropped to 20.3% (113 million people) below 2008 levels (23.7%).
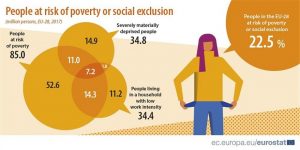
In Greece, 20.2% of the population live in poverty, 21.1% in destitution, while 15.6% live in a family facing the risk of unemployment. The corresponding average rates in the EU are 16.9%, 6.9% and 9.3%.
According to Eurostat, a person is in a state of poverty or social exclusion when he or she faces one or more of the following situations: Whether he is considered to be poor (ie he has income below 60% of the average national income), or is in a state of destitution (deprived of basic consumer goods, or fails to cope with elementary financial obligations), or lives in a family facing the risk of unemployment (ie in a family where no member has a “normal job”).
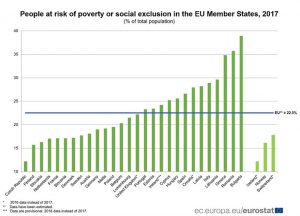
Despite the gloomy figures for Greece, it is not at the bottom of the relevant indicators, as Bulgaria (38.9%) and Romania (35.7%) are worse. The Czech Republic (12.2%), Finland (15.7%), Slovakia (16.3%), the Netherlands (17%), Slovenia and France (17.1%) and Denmark (17.2%), Sweden (17.7%), Austria (18.1%) and Germany (19%).
Reducing the number of people at risk from poverty or social exclusion in the EU is one of the key objectives of the Europe 2020 strategy.
Ask me anything
Explore related questions