Many Americans first became aware of U.S. military operations in Africa in October 2017, after the Islamic State ambushed American troops near Tongo Tongo, Niger, killing four U.S. soldiers and wounding two others.
Just after the attack, U.S. Africa Command said U.S. troops were providing “advice and assistance” to local counterparts. Later, it would become clear that those troops — the 11-man Operational Detachment-Alpha Team 3212 — were working out of the town of Oullam with a larger Nigerian force under the umbrella of Operation Juniper Shield, a wide-ranging counterterrorism effort in northwest Africa.
Until poor weather prevented it, that team was supposed to lend support to another group of American commandos who were trying to kill or capture Islamic State leader Doundoun Cheffou as part of Obsidian Nomad II.
Juniper Shield and Obsidian Nomad II were not isolated efforts but part of a panoply of named military operations and activities U.S. forces have been conducting from dozens of bases across the northern tier of Africa. Many of these operations are taking place in countries that the U.S. government does not recognize as combat zones, but in which U.S. troops are nonetheless fighting and, in several cases, taking casualties.
Between 2013 and 2017, U.S. special operations forces saw combat in at least 13 African countries, according to retired Army Brig. Gen. Don Bolduc, who served at U.S. Africa Command from 2013 to 2015 and then headed Special Operations Command Africa until 2017. Those countries, according to Bolduc, are Burkina Faso, Cameroon, Central African Republic, Chad, Democratic Republic of Congo, Kenya, Libya, Mali, Mauritania, Niger, Somalia, South Sudan and Tunisia. He added that U.S. troops have been killed or wounded in action in at least six of them: Kenya, Libya, Niger, Somalia, South Sudan and Tunisia.
Yahoo News has put together a list of three dozen such operations across the continent.
The code-named operations cover a variety of different military missions, ranging from psychological operations to counterterrorism. Eight of the named activities, including Obsidian Nomad, are so-called 127e programs, named for the budgetary authority that allows U.S. special operations forces to use certain host-nation military units as surrogates in counterterrorism missions.
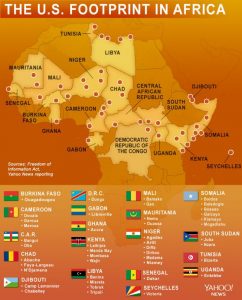
Used extensively across Africa, 127 programs can be run either by Joint Special Operations Command (JSOC), the secretive organization that controls the Navy’s SEAL Team 6, the Army’s Delta Force and other special mission units, or by “theater special operations forces.” These programs are “specifically designed for us to work with our host nation partners to develop small — anywhere between 80 and 120 personnel — counterterrorism forces that we’re partnered with,” said Bolduc. “They are specially selected partner-nation forces that go through extensive training, with the same equipment we have, to specifically go after counterterrorism targets, especially high-value targets.”
Read more HERE
Ask me anything
Explore related questions





