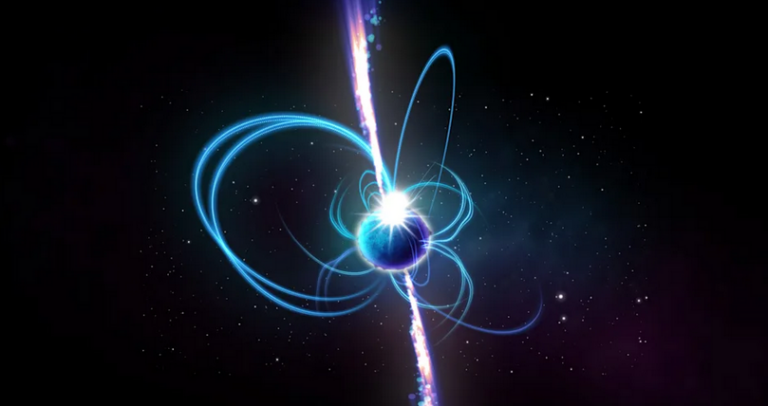
Astronomers are still finding strange objects that defy expectations. According to BBC News, researchers from the Curtin University node of the International Center for Radio Astronomy Research (ICRAR) have discovered a strange spinning Milky Way object about 4,000 light-years away. The repeating transient sent a giant burst of polarized radio energy for a full minute every 18 minutes, and was appearing and disappearing over the course of a few hours of observations — for context, a pulsar’s burst lasts a few seconds or less.
The curiosity is smaller than the Sun, but is one of the brightest radio objects in the sky during its bursts. The disappearances were also unique, according to team lead Dr. Natasha Hurley-Walker. Curtin student Tyrone O’Doherty first spotted the object using the combination of Australia’s Murchison Widefield Array and a new observation method.
There might be an existing explanation. Hurley-Walker said the data matched a predicted (but as-yet undiscovered) object known as an ultra-long period magnetar. That is, it’s a neutron star spinning at a relatively lethargic pace. Even if that’s the case, though, scientists want to know why the object is converting magnetic energy to radio waves at such an efficient rate. It could also be a white dwarf with an unusually strong magnetic field, or something else altogether.
The frenzy appears to have subsided, but Hurley-Walker is still tracking the object in case it exhibits the odd behavior again. She also plans to sift through the Murchison array’s archives to learn if there were similar objects before. Whatever this entity might be, the findings are significant — they could shape our understanding of stars and the universe at large.
Source: yahoo
Ask me anything
Explore related questions