After Russian President Vladimir Putin announced Monday that his country now regards the two long-embattled Ukrainian regions Donetsk and Luhansk as independent states and that he would station Russian troops there, the U.S. and Western allies are preparing new sanctions against Russia that are expected to be wide-ranging. While Russia has long supported separatists in the two regions to create breakaway states, the international community regards the move as an offense against Ukraine’s territorial integrity guaranteed under international law.
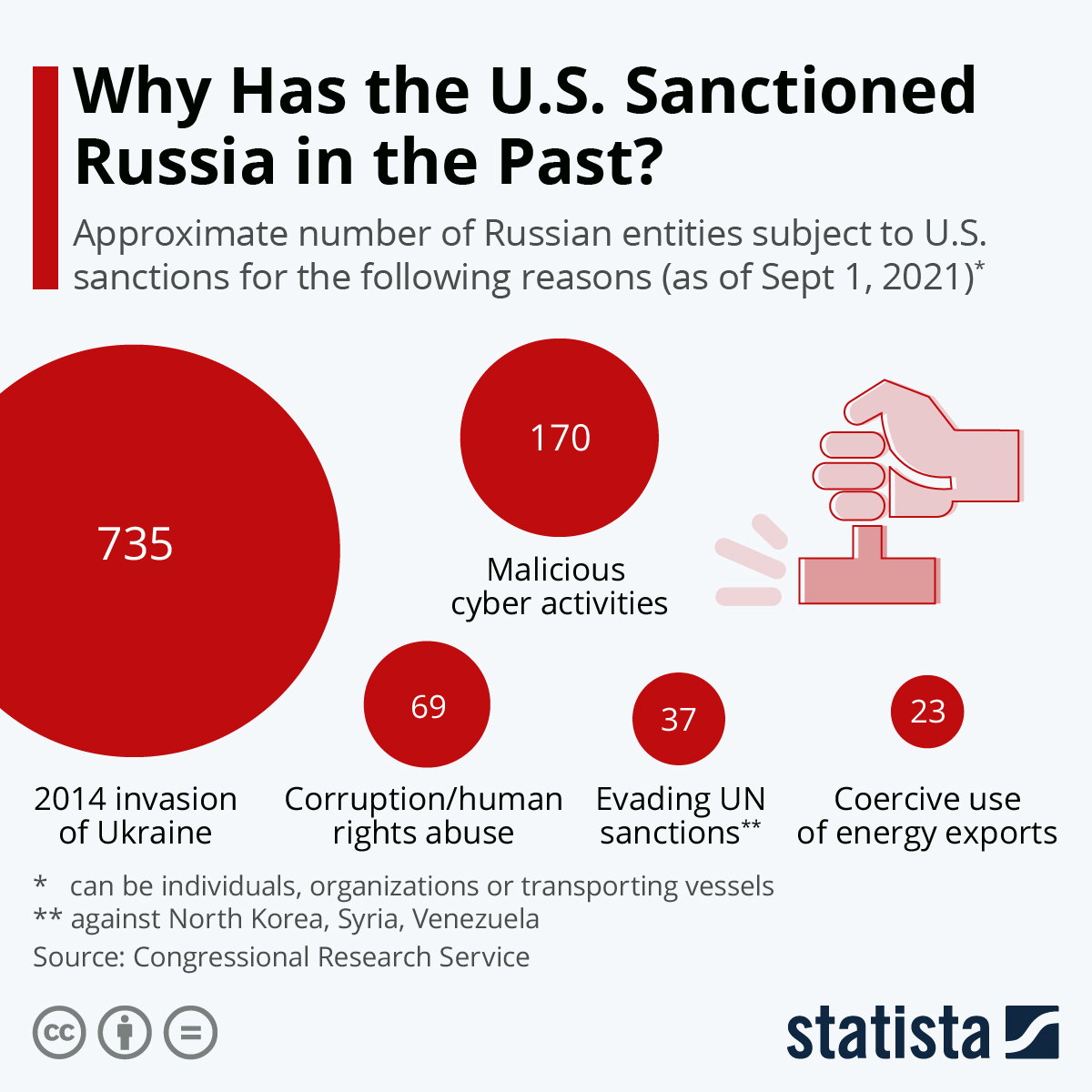
Looking at current U.S. sanctions against Russia as of September, the 2014 invasion of Ukraine and seizure of the Crimean Peninsula is the top reason why the U.S. has sanctioned Russian individuals, organizations or transportation vessels. Around 735 Russian entities are currently sanctioned in connection with the occupation of Crimea and Russian activities in Donetsk and Luhansk, where Russian military involvement also intensified after 2014.
Malicious cyber activities and influence operations are the reason the U.S. imposed sanctions against approximately 170 Russian entities. The activities include cyberattacks for financial gain or on behalf of the Russian government, for U.S. election interference and for undermining other democratic institutions.
Human rights abuse and corruption are a less common reason for sanctions. These initially were levied against those exposed for corruption by Russian lawyer Sergei Magnitsky in 2008 and thought to be responsible for this subsequent death, but have since been extended towards other human rights violators. An unspecified number of Russian entities are also sanctioned in connection with the use of chemical weapons in the poisonings of former Russian intelligence officer Sergei Skripal and others in 2018 and opposition politician Alexei Navalny in 2020. The sanctions under the U.S. Chemical and Biological Weapons Control and Warfare Elimination Act of 1991 extend to individuals and Russian government entities.
Furthermore, around 30 Russian entities – among them banks, oil traders, the state-owned arms exporter Rosoboronexport and subsidiaries of state-owned oil company Rosnef – have been sanctioned for disregarding UN sanctions against North Korea, Syria and Venezuela. Another 23 – mostly vessels – are subject to sanctions because of their involvement in the building of the Nord Stream 2 gas pipeline from Russia to Germany. The project will not become operational as its approval process has been abandoned, the German government said Tuesday.
While sanctions against organizations and vessels apply to their ability to do trade or sign business or government contracts with the U.S., sanctions against individuals can include the freezing of foreign assets or bans from travel to the United States.
You will find more infographics at Statista
Ask me anything
Explore related questions