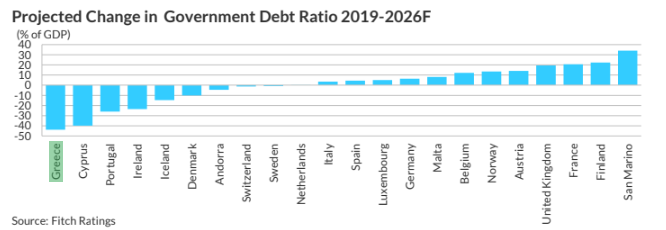
In a Europe entering 2026 with slow but notable resilience, Fitch Ratings highlights a fiscal reality that sharply differentiates the landscape. Most economies are seeing pressure on their public finances, yet Greece is placed in the small group of countries that will manage to maintain surpluses and continue reducing debt.
According to the agency, Greece will achieve the largest debt reduction in Europe from 2019 to 2026, over 40 percentage points in terms of GDP.
In the fiscal arena, the picture is clearly more difficult. Fitch notes that spending pressures are rising faster than expected, driven by defense and ageing-related costs. The EU deficit is projected to reach 2.7% of GDP in 2026, while that of the Eurozone will be close to 3%.
This is also where the “two-speed” pattern emerges. In Fitch’s forecasts, only Greece, Cyprus and Ireland are expected to post outright fiscal surpluses in 2026, while Portugal approaches balance. A common element among these countries, according to the agency, is the deep adjustment of previous years and the consistent commitment to primary surpluses even through the crises of the pandemic and the war in Ukraine.
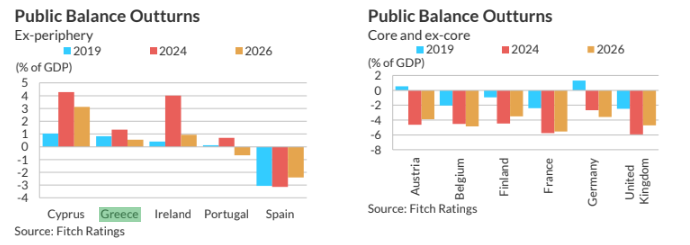
Conversely, economies with greater fiscal space—such as Germany, Denmark and Sweden—show significant deterioration due to surging defense spending. For Germany, Fitch forecasts a deficit above 4% of GDP in the coming years, levels not seen since the era of reunification.
In the case of Italy and Spain, the agency sees limited fiscal risks despite high debt, thanks to Italy’s political commitment to fiscal prudence and Spain’s strong growth momentum. By contrast, France, Belgium and the United Kingdom continue to show weak fiscal adjustment as a result of political instability and fragmentation.
Ask me anything
Explore related questions