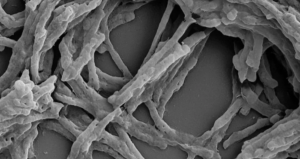
Scientists have discovered an enzyme that converts air into electricity, potentially unlocking a near-limitless source of clean energy.
A team from Monash University in Melbourne, Australia, found that a hydrogen-consuming enzyme from a common soil bacterium was able to generate an electrical current using the atmosphere as an energy source.
“We’ve known for some time that bacteria can use the trace hydrogen in the air as a source of energy to help them grow and survive, including in Antarctic soils, volcanic craters, and deep in the ocean,” said Professor Chris Greening from Monash University’s Biomedicine Discovery Institute.
What’s the smallest known asteroid? What about the largest?
“But we didn’t know how they did this, until now.”
The discovery was detailed in a paper, titled ‘Structural basis for bacterial energy extraction from atmospheric hydrogen’, published in the journal Nature on Wednesday.
Read more: yahoo
Ask me anything
Explore related questions