A new examination of two 7.2 million-year-old fossils from southern Europe suggests that humans split off from the great apes several hundred thousand years earlier than we thought.
Thanks to DNA sequencing, we know that humans and chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes) once split from a common ancestor, but there’s hot debate over the timing and location of this evolutionary parting. Now, an international team says they might have found a surprising new pre-human candidate, challenging what we think we know about early human evolution.
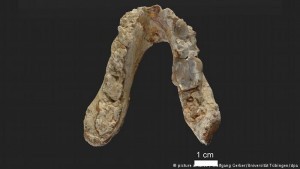
In a new study, researchers re-analysed Graecopithecus freybergi – a little-known species of dubious taxonomy originally described from a lower jaw bone fossil found in 1944 in Greece. In 2012, the Graecopithecus jaw bone was joined by a fossilised premolar found in Bulgaria.
Using micro-computed tomography and 3D reconstructions of the roots and internal structure of the fossilised teeth, the scientists found features characteristic of modern humans and their early ancestors.
They suggest this find places Graecopithecus in the hominin basket – the evolutionary branch reserved strictly for modern humans, extinct humans, and all our non-ape ancestors.
source: sciencealert.com